How to Send Email in Golang
Table of Contents
This is a series of tutorials: sending email in golang.
We’ll first start with the basic sending an email using the go command.
In the upcoming tutorials, we will create an API and a frontend using which we will send emails.
In this tutorial, we will send an email using the main.go file.
Pre-requisites #
- go v1.11 or greater - I am using go1.14.3
- Code Editor (VSCode, Atom) - I am using VS Code
- Brevo (formerly Sendinblue) account - link
Getting Started #
Create a new directory go-sendinblue.
Open the terminal inside the directory and run the below command.
go mod init go-sendinblue
This command will initiate a module go.mod.
A module is a collection of dependency modules used in the project. This will list all the dependencies with their version in the go.mod file.
Add the Dependency #
In this project, we are going to use the environment variables from the .env file. To access the .env file and use it we have to add a dependency godotenv.
go get github.com/joho/godotenv
This package is simple and clean.
Learn more about
how to use environment variables in the golang.
Create a new SMTP Key #
Sign in to your Brevo (formerly Sendinblue) account and click on SMTP & API from the top-right menu.
Go to SMTP tab and click on CREATE A NEW SMTP KEY.
Copy the key and paste it somewhere safe.
⚠️ Note: If you lose this key, then you can’t retrieve it. Then you have to create a new one and replace it accordingly.
Environment Variable #
Create a new .env file inside the go-sendinblue project.
Open the file and enter the following keys and values.
PASSWORD=Enter your Sendinblue SMTP Key
SMTP_HOST=smtp-relay.sendinblue.com
SMTP_PORT=587
Verify the SMTP_HOST and SMTP_PORT from the SMTP & API section of your account.
⚠️ Caution: If you’re using git then don’t forget to add
.envin the.gitignorefile. This will prevent your secrets to access by anyone.
Coding Time 👨💻 #
Create a new main.go inside the go-sendinblue project.
Open the main.go file and paste the below code.
We are going to use smtp package provided by golang.
Package smtp implements the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol as defined in RFC 5321.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/smtp"
"os"
// Import godotenv
"github.com/joho/godotenv"
)
func main() {
// From address
from := "hello@schadokar.dev"
// Array of recipients address
to := []string{"shubham@schadokar.dev"}
// Create a message and convert it into bytes
msg := []byte("To: shubham@schadokar.dev\r\n" +
"From: hello@schadokar.dev\r\n" +
"Subject: Hello Gophers!\r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"This is the email is sent using golang and Brevo (formerly Sendinblue).\r\n")
// Call the sendEmail function
status := sendEmail(from, to, msg)
// check if email sent successfully or not
if status {
fmt.Printf("Email sent successfully.")
} else {
fmt.Printf("Email sent failed.")
}
}
// send mail function
func sendEmail(from string, to []string, msg []byte) bool {
// Load .env file to use the environment variable
err := godotenv.Load(".env")
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Error loading .env file")
}
// Set up authentication information.
auth := smtp.PlainAuth("", from, os.Getenv("PASSWORD"), os.Getenv("SMTP_HOST"))
// format smtp address
smtpAddress := fmt.Sprintf("%s:%v", os.Getenv("SMTP_HOST"), os.Getenv("SMTP_PORT"))
// Connect to the server, authenticate, set the sender and recipient,
// and send the email all in one step.
err = smtp.SendMail(smtpAddress, auth, from, to, msg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
return false
}
// return true on success
return true
}
Let’s understand the code piece by piece.
In the main function we’re first declaring the from, to, and msg.
from is the address from which you created the Brevo (formerly Sendinblue).
to is an array of string.
msg is an array of bytes.
⚠️ You must define the From field in the msg. It is not mentioned in the smtp package documentation. Maybe it is only required for Brevo (formerly Sendinblue). I have not tested with other mail service providers.
In the sendEmail function, it is taking from, to, and msg as arguments and returning a bool status.
In the import, we have imported the github.com/joho/godotenv package to load the .env file. To load the .env file, use Load method of godoenv.
From the .env file, we will load PASSWORD, SMTP_HOST and SMTP_PORT.
The smtp package has 2 methods to authenticate the mail server.
Read more
We’re going to use the PlainAuth method.
Syntax #
func PlainAuth(identity, username, password, host string) Auth
PlainAuth returns an Auth that implements the PLAIN authentication mechanism as defined in RFC 4616. The returned Auth uses the given username and password to authenticate to host and act as identity. Usually, identity should be the empty string, to act as username.
PlainAuth will only send the credentials if the connection is using TLS or is connected to localhost. Otherwise, authentication will fail with an error, without sending the credentials.
Now, as the .env is loaded by the godotenv package. We can use os package to read the environment variables.
Format an SMTP Address.
smtp-relay.sendinblue.com:587
Use os package to read PASSWORD, SMTP_HOST and SMTP_PORT.
Using the SendMail method of smtp package, it can connect to the server, authenticate and send the email the message to all the recipients by the sender.
Send the email #
Open the project in the terminal and run the below command.
go run main.go
Check your mailbox. You have received a mail. If you could not find the mail check in the promotion.
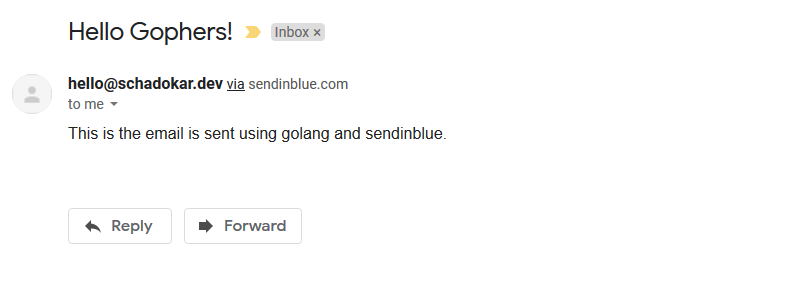
The smtp package does not provide enough information of delivery of the mail. It only confirms if mail sent to server or not.
From server side, there can be many reasons if it is delivered or not. To check if sent successfully or not.
Open the Brevo (formerly Sendinblue) account and click on the Transactional tab.
In this tab, you can check the status of the mail. The common reason can be an incorrect mail address. For this it raise a Hard bounce event.
Conclusion #
Hope, you find this tutorial helpful. The complete code is available on my GitHub repository.
In the upcoming tutorials, we are going to create API and a frontend.